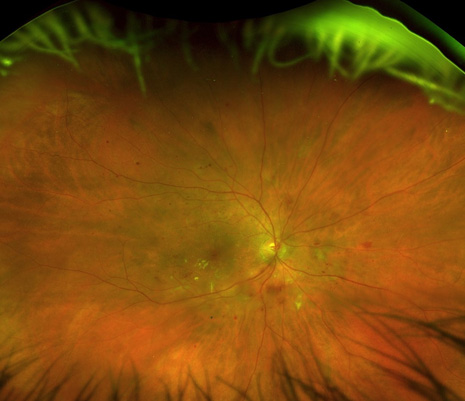
What is Diabetic Retinopathy and Maculopathy
The longer a person has diabetes, the greater their risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
High blood pressure can exacerbate the damage to blood vessels in the eyes caused by diabetes
High levels of cholesterol can contribute to the development and progression of diabetic eye disease
Understanding the complexities of diabetic eye disease and its risk factors are essential for early detection, intervention, and management to preserve vision and prevent complications. It is very important to have regular eye examinations regardless of whether you have any visual problems. This is because diabetes can gradually affect your vision and if the diabetic retinopathy is too advanced, there is a chance that it might not be treated successfully.

Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It is the most common cause of vision loss in people with diabetes.
Macular Edema: Macular edema occurs when fluid leaks into the macula, which is the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. It can result in blurred or distorted vision.
Other Complications: Diabetes can also increase the risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma
Ms Das specialises in the management of diabetic eye disease. She provides intravitreal injection treatment and laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Ms Das has a personalised approach to understand your individual medical situation and requirements and will discuss options of management, including holistic care, which might work best for you
Intravitreal Injection Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy and Maculopathy
You can reduce your risk of developing serious diabetic retinopathy
Continue to attend regular diabetic eye check-up appointments with OCT Scans and examination of the retina
Maintain your blood sugar (HbA1c), blood pressure and cholesterol at the levels agreed with your Diabetes Specialist and GP.
Exercise regularly, stay active and have a healthy diet involving portion control.
Stop smoking
Reduce alcohol consumption.
Visit www.diabetes.org.uk which has the most up to date information about the condition, diet, local social groups, and research, to help you better manage your diabetes.
Sign up to mydiabetesmyway.scot.nhs.uk, if residing in Scotland, to help you better manage your diabetes